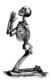
Europe: A woodcut depicting a praying skeleton, probably symbolic of the 'Black death', anon., c. 15th century
The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis.
Thought to have started in China, it travelled along the Silk Road and reached the Crimea by 1346. From there, probably carried by Oriental rat fleas living on the black rats that were regular passengers on merchant ships, it spread throughout the Mediterranean and Europe.
The Black Death is estimated to have killed 30–60 percent of Europe's population, reducing the world's population from an estimated 450 million to between 350 and 375 million in the 14th century.
The aftermath of the plague created a series of religious, social and economic upheavals, which had profound effects on the course of European history. It took 150 years for Europe's population to recover. The plague returned at various times, killing more people, until it died out in Europe in the 19th century.
Keywords:
Quick links to other images in this gallery:




Copyright © 2024, All rights reserved.






